Abstract
Objectives
The existing business-level use cases captured here have been collected and categorized to serve as initial entries into an evolving repository for and aggregator of use cases from around the world to foster development and technical standardization in this field, and to present broadcasters' expectations in developing such services.
Background
Smartphones and tablets are rapidly spreading around the world, and 80% of TV viewers in developed countries are using smartphones or tablets while watching TV programs and commercials, according to recent research.
Without any help from advanced technology, some users are simultaneously enjoying information and communication via several devices through their advanced multi-tasking skills, and some broadcasting services have been designed to appeal to these users.
Until now, there has not been a repository document that has collected and categorized existing and recognizable business-level use cases in W3C.
The future multi-screen services related to TV programs and commercials may be innovative and remarkably progressive beyond extrapolations from existing services. Even if it might be true, it would be valuable for the development and standardization of this field to collect and categorize existing business-level use cases, which captures the current actual behaviour of users.
The group is happy to work with SDOs and other groups in and around W3C to build this repository.
1. Use Cases
1.2 Package 2: Purchase products or services displayed in TV programs...
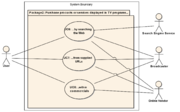
Package 2
1.2.1 UC6: ...by searching the Web
- Brief description:
- User looks for additional information on products or services displayed in TV programs by searching the Web on companion devices, then purchases the products or services via the devices.
- Primary actor:
- Stakeholders:
- Broadcaster
- Search Engine Service
- Online Vendor
- Manufacturer
- Basic flow:
- 1. User is watching a TV program on a TV set.
- 2. User is curious about a product or service displayed in the TV program.
- 3. User searches the Web for related information using Search Engine Service on a companion device. User uses key words of their own choice or from the TV program.
- 4. Search Engine Service shows a list of links on the companion device.
- 5. The list contains 1) links to manufactures' or service providers' web sites, and/or 2) links to Online Vendor that deals with the product or service, and/or 3) links to reviews of the product or service such as magazine articles, blog entries, micro-blog posts, and SNS pages.
- 6. User selects a link of interest on the companion device, learns about the product or service in detail, and purchases the product or service via Online Vendor.
1.2.2 UC7: ...from supplied URLs
- Brief description:
- User gets additional information on wineries contained in a TV program by manually inputting into a companion device URLs or by scanning QR codes displayed on the TV screen, then purchases products via the devices.
- Primary actor:
- Stakeholders:
- Broadcaster
- Online Vendor
- Manufacturer
- Basic flow:
- 1. User is watching a TV program on a TV set.
- 2. Broadcaster displays a URL or a QR code tied to a wine or winery featured in the TV program.
- 3. User inputs the URL into a companion device or scans the QR code with a QR code reader built into the device.
- 4. The companion device shows the user the web page from the URL or the QR code.
- 5. User buys the wine and/or other wines at the web site or via Online Vendor which the web page contains links to.
1.2.3 UC8: ...within commercials
- Brief description:
- User gets additional information related to commercials broadcast during TV programs by manually inputting into a companion device URLs or by scanning QR codes displayed on the TV screen, then purchases products or services the commercials feature via the devices.
- Primary actor:
- Stakeholders:
- Broadcaster
- Online Vendor
- Manufacturer
- Basic flow:
- 1. User is watching a TV program on a TV set.
- 2. Broadcaster airs a commercial during the TV program which informs the user of a URL. This is done by displaying and/or announcing the URL string. This is also done by displaying a QR code.
- 3. User inputs the URL into a companion device or scans the QR code with a QR code reader built into the device.
- 4. The companion device shows the user the web page from the URL or the QR code.
- 5. User receives additional information about the products or services.
- 6. User purchases the products or services at the web site or via Online Vendor which the web page contains links to.
1.5 Package 5: Share viewing experience with friends...
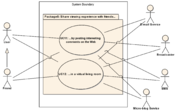
Package 5
1.5.2 UC12: ...in a virtual living room
- Brief description:
- A group of users arrange to view a TV program remotely and enjoy the program as though they were together in a living room by using e-mail, SMS or micro-blog on a companion device.
- Primary actor:
- Stakeholders:
- Broadcaster
- User/Friend
- E-mail Service
- SMS
- Micro-blog Service
- Manufacturer
- Basic flow:
- 1. A group of users plan on their companion devices to view a TV program together but remotely.
- 2. Each user starts watching the TV program on their own TV set.
- 3. The users share their impressions of scenes of interest via e-mail, SMS or micro-blog. An active dialogue between users ensues.
1.6 Package 6: Share viewing experience publicly...
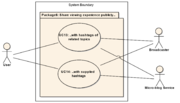
Package 6
1.7 Package 7: Watch TV programs on TV sets...
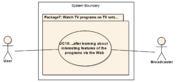
Package 7
1.7.1 UC15: ...after learning about interesting features of the programs via the Web
- Brief description:
- User comes across an enticing description about a TV program on the Web via a companion device and watches the TV program on a TV set.
- Primary actor:
- Stakeholders:
- Basic flow:
- 1. User comes across an enticing description about a TV program on the Web via a companion device.
- 2. User watches the TV program on a TV set.
- Note:
- This is a generic use case. The Web has long been providing numerous ways to discover TV content and the editors see no reason to write a use case for each specific way users can discover TV programming on the Web at the time of publication of this document.
1.8 Package 8: Participate in interactive TV programs...
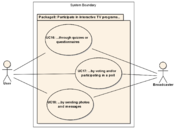
Package 8
1.8.1 UC16: ...through quizzes or questionnaires
- Brief description:
- Broadcaster provides quizzes or questionnaires on a companion as the program progresses and superimposes a selection of user responses or statistical results on TV screens.
- Primary actor:
- Stakeholders:
- Broadcaster
- Manufacturer
- Online Survey Service
- Basic flow:
- 1. User is watching an interactive TV program on a TV set.
- 2. Broadcaster promotes interactive aspects of the TV program available through a companion device application.
- 3. User activates the application to particpate interactively with the TV program on a companion device.
- 4. Broadcaster provides quizzes or questionnaires in the application as the program progresses.
- 5. User inputs their choices or answers and submits them to the broadcaster.
- 6. Broadcaster compiles the responses and superimposes a selection of the responses and/or other statistical results on TV screens.
- Note:
- Broadcaster and Online Survey Service may partner to provide this use case.
1.8.2 UC17: ...by voting and/or participating in a poll
- Brief description:
- Broadcaster invites users to cast votes and/or participate in a poll. User interacts via companion devices.
- Primary actor:
- Stakeholders:
- Broadcaster
- Manufacturer
- Online Survey Service
- Basic flow:
- 1. User is watching an interactive TV program on a TV set.
- 2. Broadcaster promotes interactive aspects of the TV program available through a companion device application.
- 3. User activates the application to participate interactively with the TV program on a companion device.
- 4. Broadcaster invites users to cast votes and/or participate in a poll.
- 5. User inputs their choices and/or answers and submits them to the broadcaster.
- 6. Broadcaster compiles the responses and superimposes a selection of the responses and/or other statistical results on TV screens.
- Note:
- Broadcaster and Online Survey Service may partner to provide this use case.
1.8.3 UC18: ...by sending photos and messages
- Brief description:
- Broadcaster displays photos and messages posted by users with companion devices.
- Primary actor:
- Stakeholders:
- Broadcaster
- Manufacturer
- Photo Sharing Service
- Basic flow:
- 1. User is watching an interactive TV program on a TV set.
- 2. Broadcaster promotes interactive aspects of the TV program available through a companion device application.
- 3. User activates the application to participate interactively with the TV program on a companion device.
- 4. Broadcaster invites users to post photos and messages.
- 5. User submits their content to the broadcaster.
- 6. Broadcaster compiles then superimposes a selection of the posts on TV screens.
- Note:
- Broadcaster and Photo Sharing Service may partner to provide this use case.
1.9 Package 9: Continue watching TV programs...
2. Using Companion Apps To Greatly Improve UX
In the broadcasting industry, companion apps are applications on any device that are specifically designed to access broadcaster resources for specific TV program metadata and time synchronisation information, which clearly improves UX of use cases above.
There are three classes of companion apps based on reach. The class of apps with the broadest reach works with all channels viewable on TV sets. The next class of apps is narrower and is applied to only one channel. Finally the last class of apps works with only one TV program.
3. Using Time-Sync Technologies To Dramatically Improve UX
The heart of TV programs and TV technologies is their temporal nature. Traditionally, the one and only UX TV has been providing is just showing the right pictures at the right time in a sufficient frequency, so it's a totally dynamic or temporal experience. By synchronising web apps' behaviours on companion devices in time with TV programs, it's clear we can experience a dramatic improvement in the UX of most use cases above.
There are two methods to provide companion devices with time-sync information from TV programs.
- Provide applications with timing information signals through in-band triggers in MPEG transport streams or out-band triggers sent from web servers via the Net.
- Provide applications with files containing all timing information so that applications synchronise using the wall-clock model [1] with TV programs.
4. Using ACR To Improve Dumb TV Set UX
4.1 Brief Introduction to ACR
The latest developments in watermarking and fingerprinting technologies are now seeing new applications enabling ACR (automatic content recognition) and also triggering specific events to smart devices. ACR for video and/or audio signals enables identification and synchronisation between broadcast, on-demand or recorded television content, and interactive applications on devices such as tablets, smartphones or laptops.
4.1.1 Package 1: UC3 Variation Using ACR
An easy way to explain the benefits of ACR is to vary an existing use case. Here we simplify Package 1: UC3 above to illustrate ACR's potential effect on our use cases.
- Package 1: UC3: Get detailed information on the Olympic Games
- Basic description:
- User receives additional information on content broadcast from the Summer Olympic Games by activating ACR apps available on companion devices.
- Basic flow:
- 1. User is watching the Summer Olympic Games on a TV set.
- 2. User activates an ACR app available on a companion device. Following the result of scene recognition by the ACR app, the companion device displays either content from the portal of the Olympic Games web site or detailed information about the sport being viewed.
- Note:
- This ACR app also contains additional links to information about the Olympic Games. User can navigate beyond the sport or the athlete by following these links.
4.2 The Potential of ACR
- Use of ACR can reduce a number of steps required for users to link to TV programs on companion devices.
- Once ACR hits critical mass, broadcasters can use ACR to synchronise a broader range of content displayed on apps even during live TV programs without the need for additional web servers and bandwidth.
5. Broadcaster's Expectation
- Multiple screens could create promising new services through their smarter combinations with TV programs and commercials. Broadcasters would expect that web apps on a TV set and web apps on a companion device could link, connect and interact with each other to enable creating innovative TV programs and commercials easily.
- TV broadcasting is one of mass communication media, which is good at delivering same content and services to all TV sets in its region efficiently. To make good use of this nature of TV broadcasting, broadcasters would expect that mechanisms to cope with connecting any kind of TV sets with any kind of companion devices easily would be provided.
A. Acknowledgements
Thanks to Tim Berners-Lee for inventing HTML, without which none of this would exist.
The editors would like to thank Olivier Thereaux and Jean-Charles Verdié for their contributions to this note.